1. Mehta RL, Pascual MT, Soroko S, et al. Spectrum of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit: the PICARD experience.
Kidney Int 2004;66:1613–1621.


2. Hoste EA, Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: the multinational AKI-EPI study.
Intensive Care Med 2015;41:1411–1423.


3. Jones CH, Richardson D, Goutcher E, et al. Continuous venovenous high-flux dialysis in multiorgan failure: a 5-year single-center experience.
Am J Kidney Dis 1998;31:227–233.


4. Douma CE, Redekop WK, van der Meulen JH, et al. Predicting mortality in intensive care patients with acute renal failure treated with dialysis.
J Am Soc Nephrol 1997;8:111–117.


5. Silvester W, Bellomo R, Cole L. Epidemiology, management, and outcome of severe acute renal failure of critical illness in Australia.
Crit Care Med 2001;29:1910–1915.


6. Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study.
JAMA 2005;294:813–818.


7. Tolwani A. Continuous renal-replacement therapy for acute kidney injury.
N Engl J Med 2012;367:2505–2514.


8. Bagshaw SM, Darmon M, Ostermann M, et al. Current state of the art for renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury.
Intensive Care Med 2017;43:841–854.


9. Oppert M, Engel C, Brunkhorst FM, et al. Acute renal failure in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: a significant independent risk factor for mortality: results from the German Prevalence Study.
Nephrol Dial Transplant 2008;23:904–909.


10. Kim WY, Huh JW, Lim CM, Koh Y, Hong SB. Analysis of progression in risk, injury, failure, loss, and end-stage renal disease classification on outcome in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock.
J Crit Care 2012;27:104.

11. Bouchard J, Soroko SB, Chertow GM, et al. Fluid accumulation, survival and recovery of kidney function in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury.
Kidney Int 2009;76:422–427.


12. Messmer AS, Zingg C, Müller M, Gerber JL, Schefold JC, Pfortmueller CA. Fluid overload and mortality in adult critical care patients-a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.
Crit Care Med 2020;48:1862–1870.


13. Silversides JA, Fitzgerald E, Manickavasagam US, et al. Deresuscitation of patients with iatrogenic fluid overload is associated with reduced mortality in critical illness.
Crit Care Med 2018;46:1600–1607.


14. Prowle JR, Echeverri JE, Ligabo EV, Ronco C, Bellomo R. Fluid balance and acute kidney injury.
Nat Rev Nephrol 2010;6:107–115.


15. Piccoli A, Pittoni G, Facco E, Favaro E, Pillon L. Relationship between central venous pressure and bioimpedance vector analysis in critically ill patients.
Crit Care Med 2000;28:132–137.


16. Tripepi G, Mattace-Raso F, Mallamaci F, et al. Biomarkers of left atrial volume: a longitudinal study in patients with end stage renal disease.
Hypertension 2009;54:818–824.


17. Trezzi M, Torzillo D, Ceriani E, et al. Lung ultrasonography for the assessment of rapid extravascular water variation: evidence from hemodialysis patients.
Intern Emerg Med 2013;8:409–415.


18. Vitturi N, Dugo M, Soattin M, et al. Lung ultrasound during hemodialysis: the role in the assessment of volume status.
Int Urol Nephrol 2014;46:169–174.


19. Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference.
Intensive Care Med 2003;29:530–538.


20. Lopes JA, Jorge S. The RIFLE and AKIN classifications for acute kidney injury: a critical and comprehensive review.
Clin Kidney J 2013;6:8–14.


21. Druml W. Acute renal failure is not a “cute” renal failure!
Intensive Care Med 2004;30:1886–1890.


22. Waikar SS, Curhan GC, Wald R, McCarthy EP, Chertow GM. Declining mortality in patients with acute renal failure, 1988 to 2002.
J Am Soc Nephrol 2006;17:1143–1150.


23. Bagshaw SM, Brophy PD, Cruz D, Ronco C. Fluid balance as a biomarker: impact of fluid overload on outcome in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury.
Crit Care 2008;12:169.


24. Garzotto F, Ostermann M, Martín-Langerwerf D, et al. The Dose Response Multicentre Investigation on Fluid Assessment (DoReMIFA) in critically ill patients.
Crit Care 2016;20:196.



25. Vaara ST, Korhonen AM, Kaukonen KM, et al. Fluid overload is associated with an increased risk for 90-day mortality in critically ill patients with renal replacement therapy: data from the prospective FINNAKI study.
Crit Care 2012;16:R197.



26. Woodward CW, Lambert J, Ortiz-Soriano V, et al. Fluid overload associates with major adverse kidney events in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury requiring continuous renal replacement therapy.
Crit Care Med 2019;47:e753–e760.


27. Prowle JR, Bellomo R. Continuous renal replacement therapy: recent advances and future research.
Nat Rev Nephrol 2010;6:521–529.


28. Perren A, Markmann M, Merlani G, Marone C, Merlani P. Fluid balance in critically ill patients. Should we really rely on it?
Minerva Anestesiol 2011;77:802–811.

29. Claure-Del Granado R, Mehta RL. Fluid overload in the ICU: evaluation and management.
BMC Nephrol 2016;17:109.



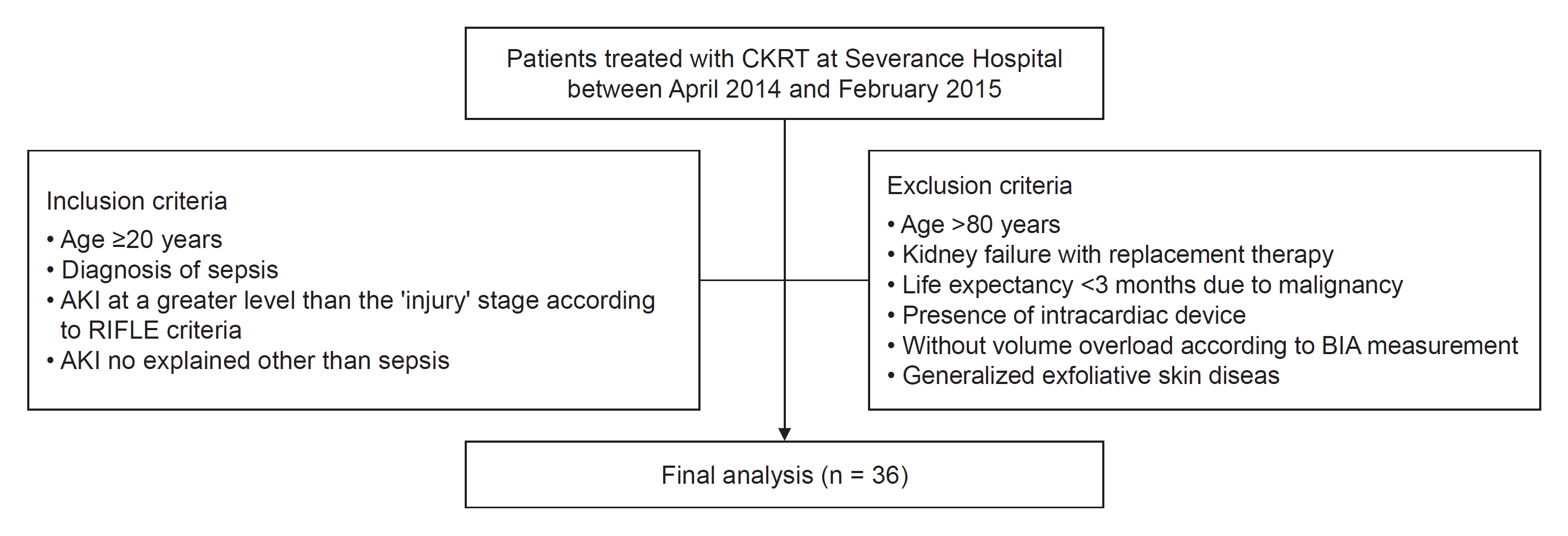
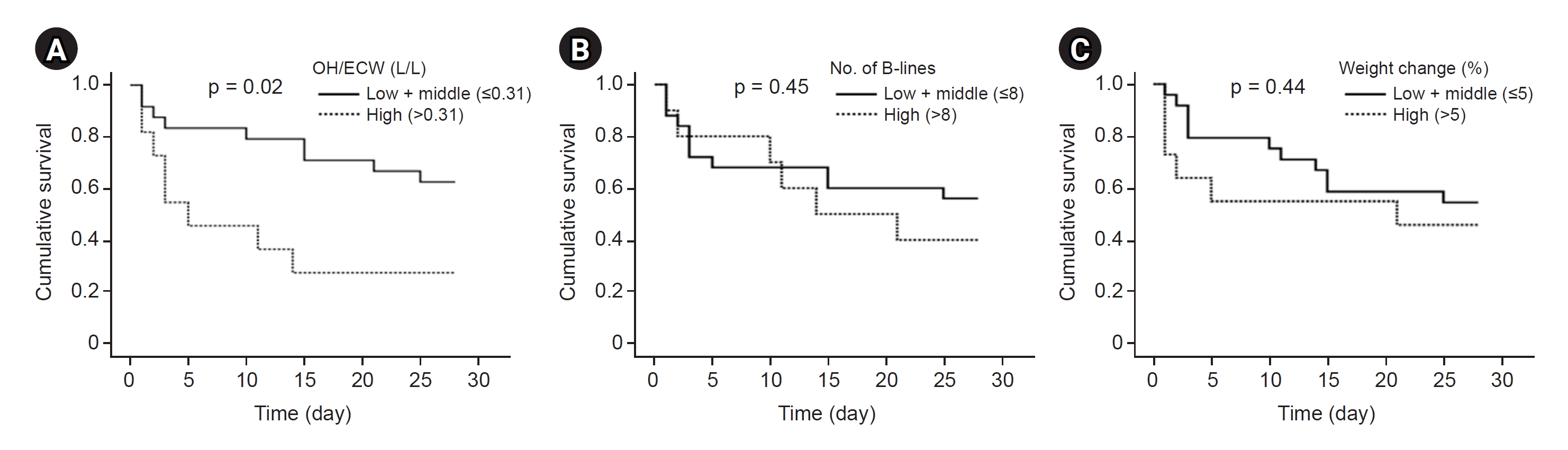
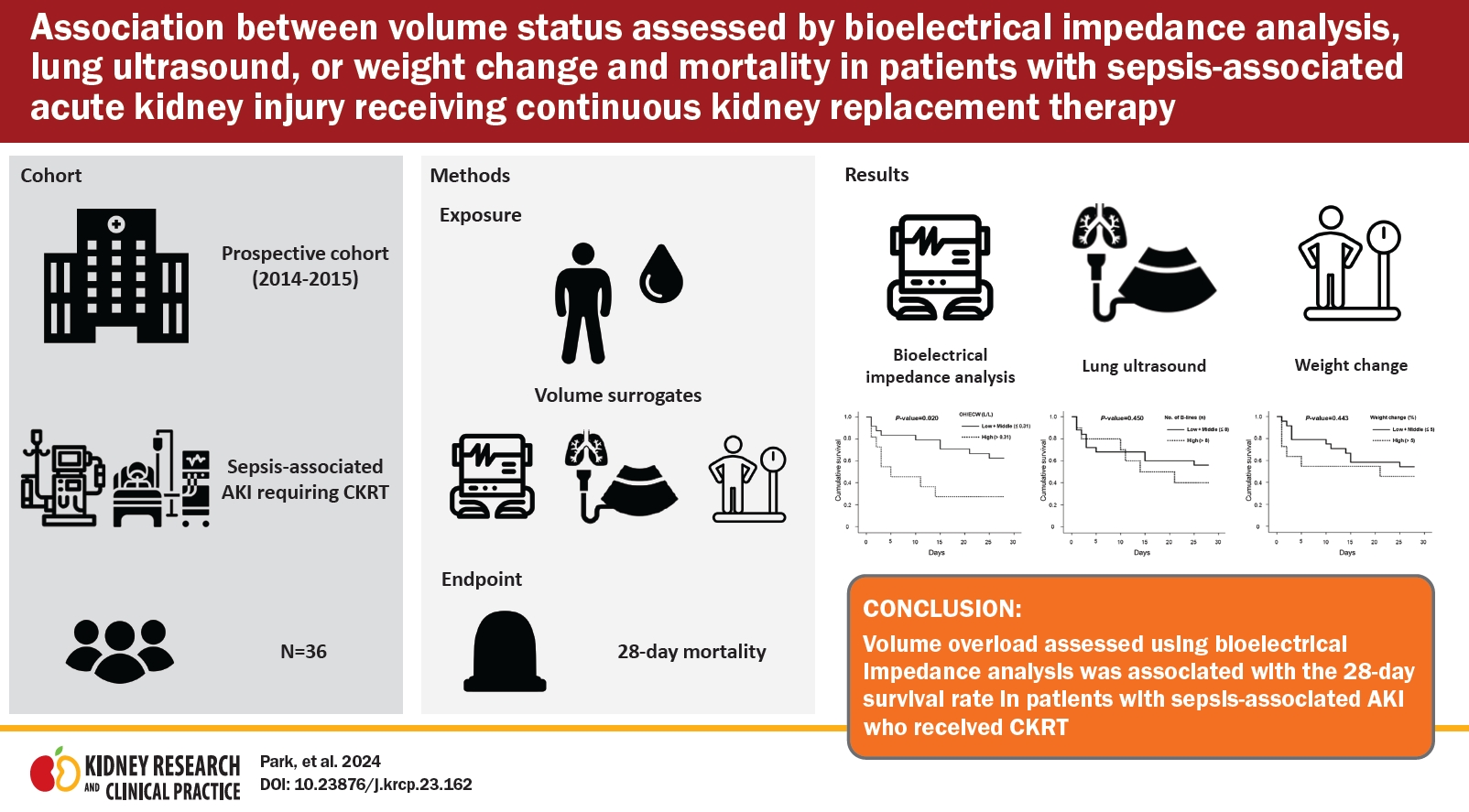
30. Kim JS, Han BG. Assessment of body fluid in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury requiring continuous renal replacement therapy.
Kidney Res Clin Pract 2020;39:381–383.



31. Wu B, Zhang S, Wang J, et al. Ratio of overhydration and extracellular water versus ratio of extracellular water and body cell mass in the assessment of fluid status in patients with acute kidney injury requiring kidney replacement therapy: a cohort study.
J Ren Nutr 2022;32:152–160.













 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement table 1
Supplement table 1 Print
Print















