| Kidney Res Clin Pract > Volume 39(4); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Acknowledgments
Notes
Funding
This research was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant no. HC15C1129).
Authors’ contributions
Jong Hyun Jhee, Jae Yoon Park, Dong Ki Kim, Seung Hyeok Han, Tae-Hyun Yoo, Shin-Wook Kang, and Jung Tak Park participated in the data collection. Jong Hyun Jhee, Jae Yoon Park and wrote the manuscript. Jung Pyo Lee and Jung Tak Park participated in the study design. Jong Hyun Jhee, Jae Yoon Park, Jung Nam An performed the statistical analysis. Jong Hyun Jhee, Jae Yoon Park, Jung Pyo Lee, and Jung Tak Park participated in the conception, analysis, and interpretation of data. Kwon Wook Joo, Yun Kyu Oh, Chun Soo Lim, Yon Su Kim, and Shin-Wook Kang participated in the study design and coordination and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Figure 1
Kaplan-Meier curves for all-cause mortality compared between the fluid overload (FO) and no fluid overload (NFO) groups before (A) and after (B) propensity score-matching.

Figure 2
Kaplan-Meier curves for 28-day mortality compared between the fluid overload (FO) and no fluid overload (NFO) groups before (A) and after (B) propensity score-matching.
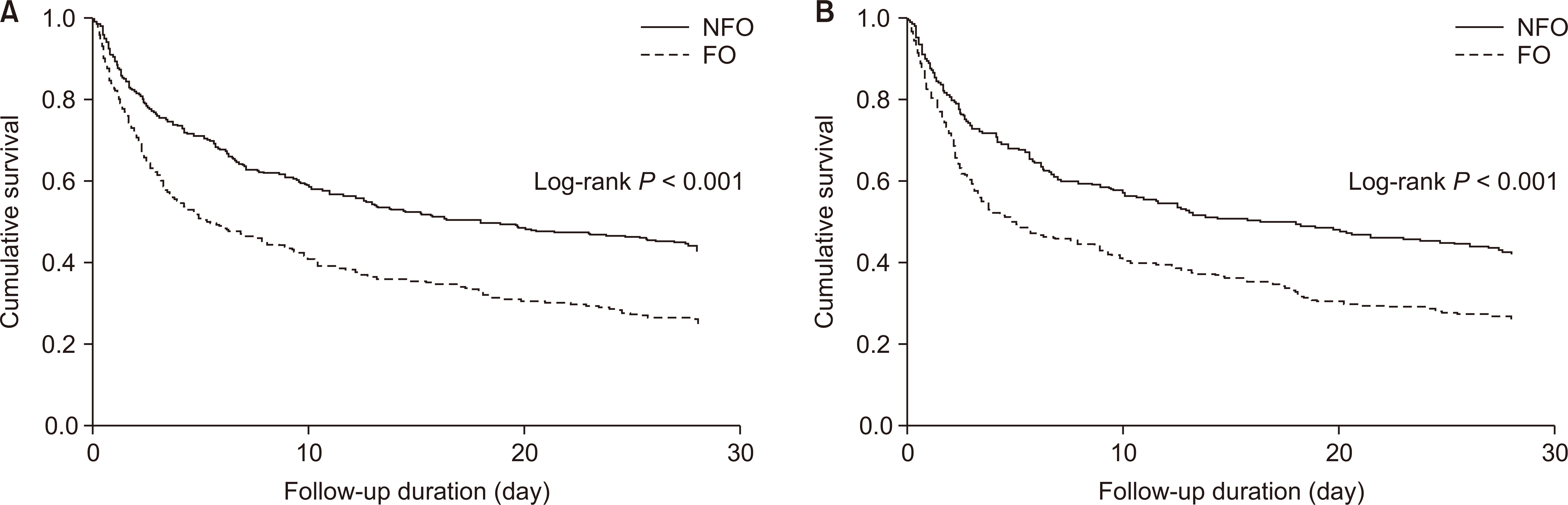
Figure 3
Subgroup analysis stratified by causes of acute kidney injury (AKI) and severity of disease.
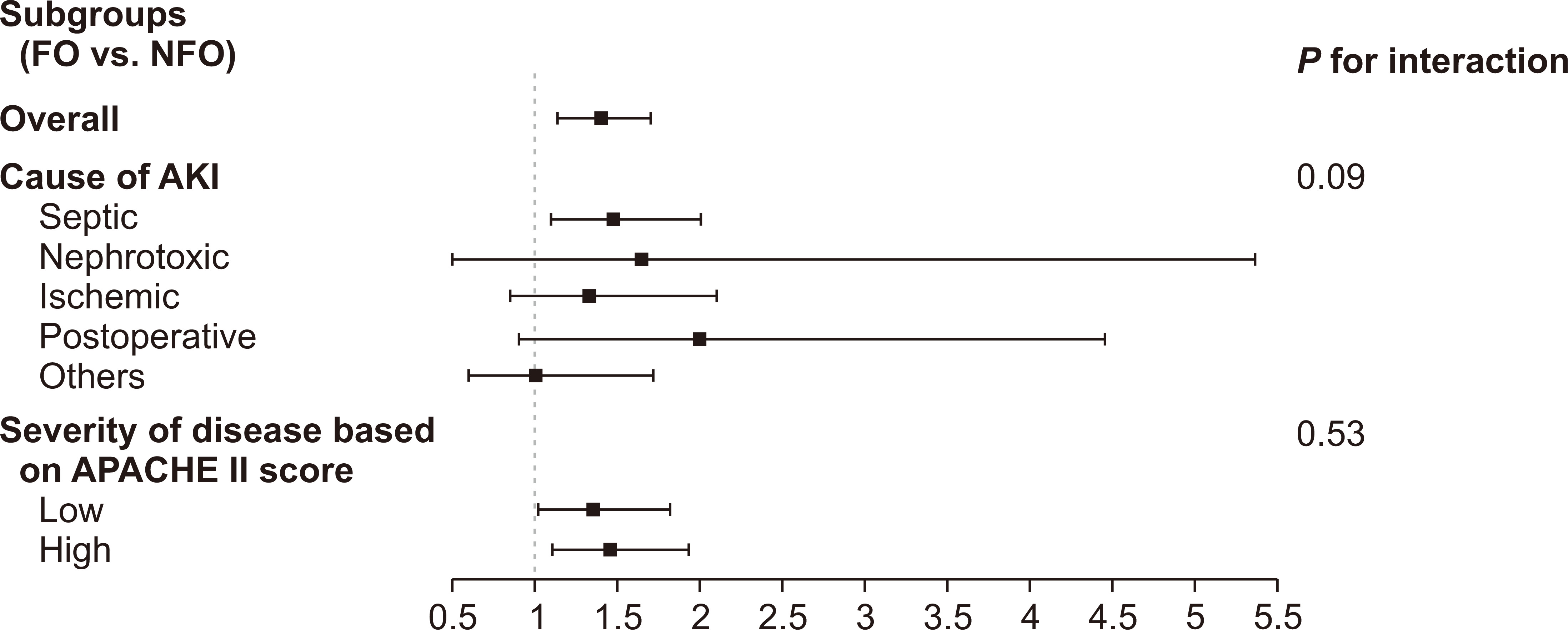
Table 1
The data are presented as median (interquartile range), number (percentage), or as mean ± standard deviation.
APACHE II, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; CRRT, continuous renal-replacement therapy; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; FiO2, inspired oxygen fraction; FO, fluid overload; ICU, intensive care unit; NFO, no fluid overload; PT-INR, prothrombin time–international normalized ratio, PSM, propensity score-matching; SD, standardized difference; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
Table 2
| Group | Model 1a | Model 2b | Model 3c | Model 4d | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | ||||
| NFO | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | |||||||
| FO | 1.74 (1.45-2.08) | < 0.001 | 1.71 (1.42-2.05) | < 0.001 | 1.38 (1.13-1.89) | < 0.001 | 1.59 (1.31-1.94) | < 0.001 | |||
aUnadjusted model. bAdjusted for age, sex, and Charlson comorbidity index (CCI). cModel 2 + systolic blood pressure (SBP), serum albumin, creatinine, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score, use of diuretics, and mechanical ventilation status. dPropensity score-matched; covariates for matching: age, sex, CCI, SBP, and serum creatinine level.
Table 3
Table 4
| Variable | Model 1a | Model 2b | Model 3c | Model 4d | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value | ||||
| Low FO% | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | |||||||
| High FO% | 1.76 (1.47–2.12) | < 0.001 | 1.75 (1.46–2.10) | < 0.001 | 1.42 (1.16–1.74) | 0.001 | 1.69 (1.40–2.064) | < 0.001 | |||
FO% was defined by the percentage of fluid accumulation by dividing CFB in liters by the patient’s body weight at ICU admission and multiplying by 100%.
aUnadjusted model. bAdjusted for age, sex, and Charlson comorbidity index (CCI). cModel 2 + systolic blood pressure (SBP), serum albumin, creatinine, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score, use of diuretics, and mechanical ventilation status. dPropensity score-matched; covariates for matching: age, sex, CCI, SBP, and serum creatinine level.




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print
















