| Kidney Res Clin Pract > Volume 41(1); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Notes
Authors’ contributions
Conceptualization: YKL, JWN
Data curation: JHK, KSY
Formal analysis: SRC, HCP
Funding acquisition: YKL
Investigation: SRC, HCP, YKL, MKK
Methodology: DHK, AC
Project administration: YKL
Visualization: SRC, HCP
Writing–Original Draft: SRC, HCP, YKL
Writing–Review & Editing: All authors
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Figure 1.
Flow diagram summarizing the process of patient enrollment and follow-up.
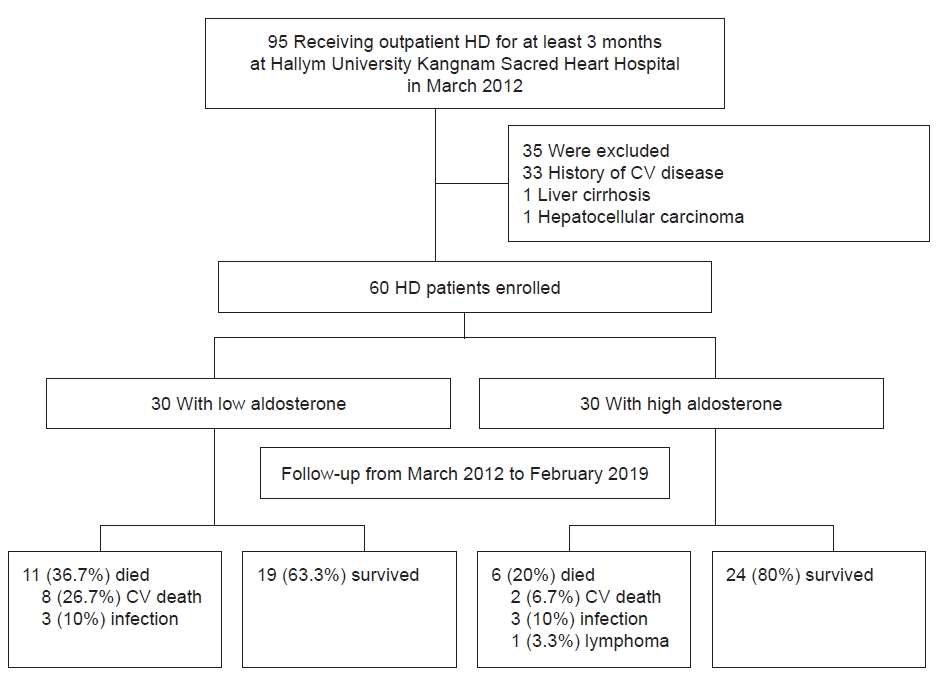
Figure 2.
Correlations between log-aldosterone and E/e' ratio and log-aldosterone and serum albumin.

Figure 3.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves for cardiovascular mortality according to the medians of log-aldosterone.

Table 1.
| Characteristic | All | Low aldosterone group | High aldosterone group | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic data | ||||
| No. of patients | 60 | 30 | 30 | |
| Age (yr) | 57.9 ± 12.1 | 60.3 ± 13.2 | 55.5 ± 10.6 | 0.13 |
| Male sex | 18 (30.0) | 8 (26.7) | 10 (33.3) | 0.40 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 30 (50.0) | 15 (50.0) | 15 (50.0) | >0.99 |
| Hypertension | 49 (81.7) | 27 (90.0) | 22 (73.3) | 0.18 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 143.4 ± 11.4 | 144.8 ± 10.1 | 141.9 ± 12.6 | 0.36 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 82.1 ± 7.2 | 83.3 ± 6.2 | 80.7 ± 7.9 | 0.20 |
| Dialysis vintage (yr) | 4.7 ± 4.6 | 4.0 ± 3.8 | 5.4 ± 5.3 | 0.25 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.3 ± 3.4 | 21.5 ± 3.1 | 23.2 ± 3.4 | 0.06 |
| Kt/V | 1.58 ± 0.26 | 1.58 ± 0.21 | 1.57 ± 0.31 | 0.85 |
| Laboratory data | ||||
| Log-aldosterone | 3.8 ± 1.4 | 2.8 ± 1.2 | 4.8 ± 0.8 | <0.001 |
| Aldosterone (ng/dL)a | 44.0 (0.1–1,210.4) | 23.0 (0.1–44.0) | 96.8 (47.5–1,210.4) | 0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.0 ± 0.9 | 9.8 ± 0.8 | 10.3 ± 1.0 | 0.07 |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 2.1 ± 1.9 | 2.0 ± 1.8 | 2.2 ± 2.1 | 0.68 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.0 ±0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 4.1 ± 0.3 | 0.008 |
| iPTH (pg/mL) | 204.3 ± 302.7 | 197.9 ± 384.9 | 210.8 ± 195.3 | 0.87 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 137.9 ± 3.1 | 137.9 ± 3.2 | 137.9 ± 3.1 | 0.94 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 4.6 ± 0.7 | 4.5 ± 0.7 | 4.7 ± 0.7 | 0.13 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 8.3 ± 0.8 | 8.2 ± 0.7 | 8.5 ± 0.9 | 0.28 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 4.8 ± 1.4 | 4.6 ± 1.3 | 5.1 ± 1.4 | 0.18 |
| Total CO2 (mmol/L) | 19.5 ± 2.1 | 19.8 ± 1.8 | 19.1 ± 2.4 | 0.19 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 154.8 ± 32.7 | 150.1 ± 26.9 | 159.4 ± 37.4 | 0.28 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 108.4 ± 70.9 | 91.5 ± 51.8 | 125.2 ± 83.4 | 0.07 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 43.4 ± 13.7 | 43.1 ± 12.5 | 43.7 ± 14.9 | 0.86 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 87.0 ± 27.3 | 85.5 ± 20.9 | 88.6 ± 32.8 | 0.66 |
| Current medicationb | ||||
| Aspirin | 46 (76.7) | 23 (76.6) | 23 (76.6) | >0.99 |
| ACEI or ARB | 44 (73.3) | 24 (80.0) | 20 (66.7) | 0.24 |
| High dose | 28 (63.7) | 17 (70.8) | 11 (55.0) | 0.35 |
| Calcium channel blocker | 39 (65.0) | 23 (76.7) | 16 (53.3) | 0.10 |
| Beta-blocker | 33 (55.0) | 20 (66.7) | 13 (43.3) | 0.12 |
| Statin | 5 (8.3) | 2 (6.7) | 3 (8.3) | >0.99 |
| IDWG (kg) | 2.5 ± 1.2 | 2.4 ± 1.1 | 2.5 ± 1.3 | 0.88 |
| IDWG% | 4.5 ± 2.2 | 4.7 ± 2.3 | 4.3 ± 2.2 | 0.46 |
| Excessive IDWG | 34 (56.7) | 17 (56.7) | 17 (56.7) | >0.99 |
Data are expressed as number only, mean ± standard deviation, number (%), or median (interquartile range).
ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IDWG, interdialytic weight gain; iPTH, intact parathyroid hormone; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Table 2.
Data are expressed as number only, mean ± standard deviation, or number (%).
ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; DW, dry weight; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IDWG, interdialytic weight gain; iPTH, intact parathyroid hormone; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Table 3.
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation or number (%).
LAD, left atrial dimension; LAVI, left atrial volume index; LVDd, end-diastolic left ventricular dimension; IVSd, interventricular septum thickness at end-diastole; PWd, posterior wall thickness at end-diastole; PAP, pulmonary artery pressure; LVMI, left ventricular mass index; LVH, left ventricular hypertrophy; E, early diastolic mitral inflow velocity; e', early diastolic mitral annular velocity; LVDD, left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; EF, ejection fraction; LVSD, left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
Table 4.
ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; CI, confidence interval; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; IDWG, intradialytic weight gain; LAD, left atrial dimension; LVDD, left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; LVMI, left ventricular mass index; OR, odds ratio; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Covariates with p-values of <0.05 upon univariate analysis (n = 3) were included in the multivariate logistic analysis model, which used an enter method.
Table 5.
ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; CCB, calcium channel blocker; CI, confidence interval; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; E, early diastolic mitral inflow velocity; e', early diastolic mitral annular velocity; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IDWG, intradialytic weight gain; OR, odds ratio; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Covariates with p-values < 0.05 upon univariate analysis (n = 4), hs-CRP and use of ACEI/ARB were included in the multivariate logistic analysis model, method with enter.
References
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 3,444 View
- 76 Download
- ORCID iDs
-
Sun Ryoung Choi

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9668-3349Young-Ki Lee

https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3464-6144Hayne Cho Park

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1128-3750Do Hyoung Kim

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8664-8830AJin Cho

https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7097-7026Juhee Kim

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2194-6327Kyu Sang Yun

https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8019-3938Jung-Woo Noh

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1743-4695Min-Kyung Kang

https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3838-951X - Related articles
-
The Effects of Low Sodium Dialysate in Hemodialysis Patients2011 January;30(1)
Heart Rate Variability in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients2011 November;30(6)
Anatomical Variation of Internal Jugular Vein in Korean Hemodialysis Patients2010 May;29(3)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement 1
Supplement 1 Print
Print















