| Kidney Res Clin Pract > Volume 38(3); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Notes
AuthorsŌĆÖ contributions
Jung Eun Lee was involved in study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation of results and review of the manuscript. Suhyun Kim and Mi Jeoung Kim were involved in data collection, analysis, interpretation of results and writing of the manuscript. Jeunseok Jeon and Hye Ryoun Jang contributed to conception, analysis and interpretation of data. Kwang Bo Park and Wooseong Huh and Young Soo Do were involved in data collection and reviewed the manuscript and provided comments. Yoon-Goo Kim and Dae Joong Kim and Ha Young Oh contributed to analysis and interpretation of data and revision of the article for important scientific content. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
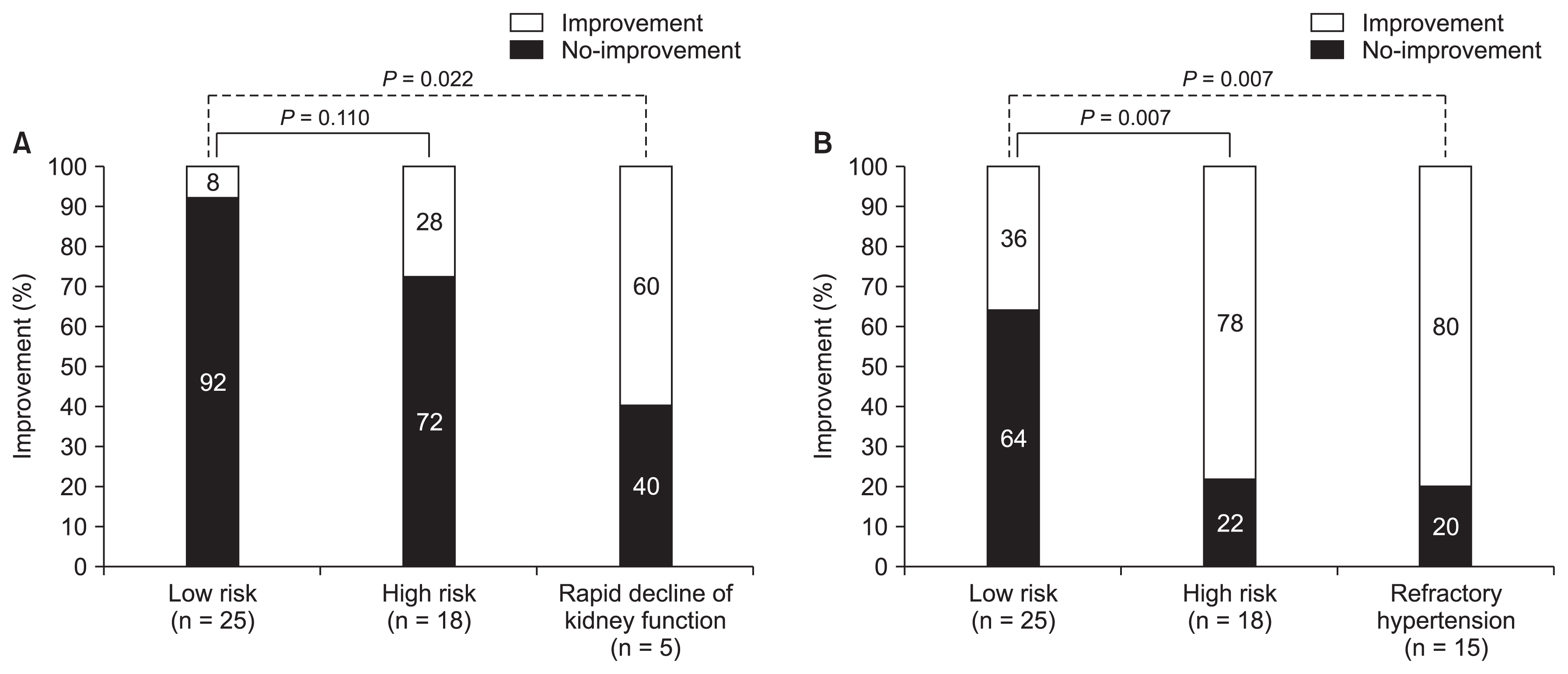
Figure┬Ā1
Proportion of subjects who showed kidney function improvement (A) or improvement of hypertension (B) at 4 months (┬▒ 1 month) after percutaneous transluminal angioplasty with stent insertion.
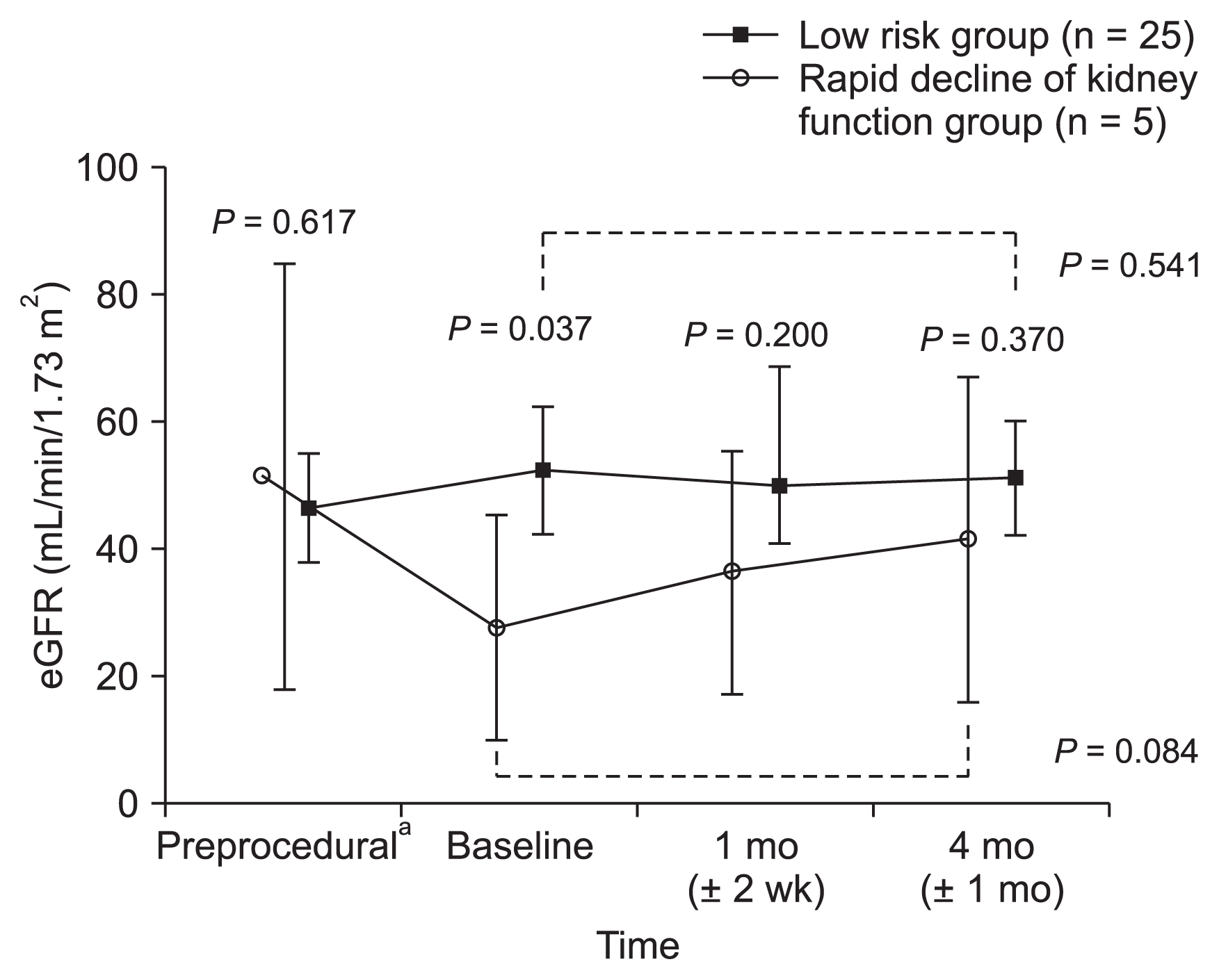
Figure┬Ā2
Change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) after renal revascularization.
Figure┬Ā3
Changes in systolic blood pressure (SBP) (A), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (B), and blood pressure medical score (BPMS) (C) after revascularization.

Table┬Ā1
| Variable | Low-risk (n = 26) | High-risk (n = 21) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 68 (58ŌĆō76) | 66 (61ŌĆō75) | 0.983 |
| Sex, male | 20 (76.9) | 15 (71.4) | 0.668 |
| Smoking | 9 (34.6) | 11(52.4) | 0.221 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.4 (21.8ŌĆō25.6) | 24.0 (22.0ŌĆō25.3) | 0.591 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 134 (122ŌĆō141) | 152 (143ŌĆō160) | 0.188 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76 (68ŌĆō80) | 77 (69ŌĆō88) | < 0.001 |
| Comorbidity | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 11 (42.3) | 13 (61.9) | 0.181 |
| CAD | 16 (61.5) | 9 (42.9) | 0.202 |
| PAD | 3 (11.5) | 7 (33.3) | 0.086 |
| Stroke | 7 (26.9) | 4 (19.0) | 0.731 |
| Baseline eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 49 (34ŌĆō64) | 33 (20ŌĆō47) | 0.046 |
| < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 3 (11.5) | 10 (47.6) | 0.006 |
| ╬öeGFRa | ŌłÆ1.3 (ŌłÆ4.4 to ŌłÆ2.7) | ŌłÆ4.9 (ŌłÆ17.1 to ŌłÆ1.6) | 0.011 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4.1 (3.8ŌĆō4.4) | 3.8 (3.6ŌĆō4.2) | 0.118 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 149 (127ŌĆō168) | 149 (132ŌĆō175) | 0.352 |
| uPCR (mg/mgCr) | 0.21 (0.09ŌĆō0.52) | 0.31 (0.00ŌĆō0.93) | 0.163 |
| Targeted kidney size (cm) | 10.0 (9.0ŌĆō10.2) | 9.8 (9.3ŌĆō10.2) | 0.703 |
| Contralateral kidney size (cm) | 10.0 (9.1ŌĆō10.0) | 9.6 (8.5ŌĆō10.0) | 0.411 |
| Targeted arterial stenosis | 0.108 | ||
| > 95% | 4 (15.4) | 1 (4.8) | |
| 75ŌĆō95% | 18 (69.2) | 19 (90.5) | |
| < 75% | 4 (15.4) | 0 (0) | |
| Bilateral stent insertion | 2 (7.7) | 6 (28.6) | 0.115 |
| Concomitant medication | |||
| ACEi/ARB | 8 (30.8) | 9 (42.9) | 0.391 |
| Diuretics | 7 (26.9) | 15 (71.4) | 0.002 |
| CCB | 18 (69.2) | 14 (66.7) | 0.851 |
| Beta blocker | 13 (50.0) | 18 (85.7) | 0.010 |
| Alpha blocker | 2 (7.7) | 1 (4.8) | 1.000 |
| Other anti-hypertensive drug | 2 (7.7) | 1 (4.8) | 1.000 |
| BPMS | 1.5 (1.0ŌĆō3.0) | 2.5 (1.8ŌĆō4.5) | 0.020 |
ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; BPMS, blood pressure medical score; CAD, coronary artery disease; CCB, calcium channel blocker; Cr, creatinine; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; PAD, peripheral artery disease; SBP, systolic blood pressure; uPCR, urine protein-to-creatinine ratio.
Table┬Ā2
| Variable | Responder (n = 25) | Non-responder (n = 18) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 66 (59ŌĆō75) | 69 (58ŌĆō75) | 0.803 |
| Sex, male | 20 (80.0) | 12 (66.7) | 0.480 |
| Smoking | 12 (48.0) | 6 (33.3) | 0.336 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.1 (21.8ŌĆō25.5) | 23.2 (21.9ŌĆō26.3) | 0.674 |
| Concurrent medication | |||
| ACEi/ARB | 11 (44.0) | 5 (27.8) | 0.278 |
| Diuretics | 12 (48.0) | 11 (61.1) | 0.553 |
| CCB | 16 (64.0) | 13 (72.2) | 0.570 |
| Beta blocker | 17 (68.0) | 12 (66.7) | 0.927 |
| Alpha blocker | 2 (8.0) | 1 (5.6) | 1.000 |
| Statin | 16 (64.0) | 15 (83.3) | 0.163 |
| Aspirin | 19 (76.0) | 11 (61.1) | 0.294 |
| Clopidogrel | 12 (48.0) | 6 (33.3) | 0.336 |
| Other antiplatelet | 1 (4.0) | 1 (5.6) | 1.000 |
| Warfarin | 5 (20.0) | 5 (27.8) | 0.717 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 150 (132ŌĆō156) | 138 (125ŌĆō145) | 0.047 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 80 (69ŌĆō89) | 74 (68ŌĆō80) | 0.054 |
| BPMS | 2.3 (1.4ŌĆō4.0) | 1.8 (1.0ŌĆō3.0) | 0.190 |
| Baseline eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 39 (24ŌĆō58) | 44 (30ŌĆō58) | 0.961 |
| < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 7 (28.0) | 4 (22.2) | 0.736 |
| ╬öeGFRa | ŌłÆ3.9 (ŌłÆ10.7 to ŌłÆ0.7) | ŌłÆ1.3 (ŌłÆ4.2 to ŌłÆ1.7) | 0.050 |
| uPCR (mg/mgCr) | 0.20 (0.08ŌĆō0.42) | 0.31 (0.06ŌĆō0.95) | 0.117 |
| Proteinuriab (g/gCr) | 0.679 | ||
| < 1 | 20 (87.0) | 14 (77.8) | |
| Ōēź 1 | 3 (13.0) | 4 (22.2) | |
| Contralateral kidney sizec (cm) | 10.0 (9.1ŌĆō10.0) | 9.4 (8.9ŌĆō10.0) | 0.379 |
| 7.5ŌĆō8.5 | 3 (17.6) | 2 (15.4) | 1.000 |
| Targeted kidney size (cm) | 9.9 (9.3ŌĆō10.1) | 10.0 (8.9ŌĆō10.2) | 0.959 |
| 7.5ŌĆō8.5 | 2 (8.0) | 2 (11) | 1.000 |
| Targeted arterial stenosisd | 89 (80ŌĆō95) | 85 (74ŌĆō95) | 0.183 |
| > 95% | 3 (12.5) | 2 (11.1) | |
| 75ŌĆō95% | 21 (87.5) | 12 (66.7) | 0.040 |
| < 75% | 0 (0) | 4 (22.2) | |
| Bilateral stent insertion | 5 (20.0) | 3 (16.7) | 1.000 |
| Low-risk/high-risk | 10 (40.0)/15 (60.0) | 15 (83.3)/3 (16.7) | 0.004 |
| Refractory hypertension | 13 (52.0) | 2 (11.1) | 0.006 |
| Rapid decline of kidney function | 5 (20.0) | 0 (0) | 0.064 |
ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; BPMS, blood pressure medical score; CCB, calcium channel blocker; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; uPCR, urine protein-to-creatinine ratio.
a Median change in kidney function between baseline eGFR and pre-procedural eGFR. The pre-procedural eGFR is the result of the last examination within six months prior to the PTA/S.
b Data regarding baseline uPCR were not routinely collected. Total number of responders was 23 due to missing data for two subjects.
c Data regarding contralateral kidney size were not routinely measured. Total numbers of responders and non-responders were 17 and 13, respectively, due to missing data for 13 subjects.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print
















